Albuterol Sulfate Elixir Dispenser

Pediatric Dosing Information
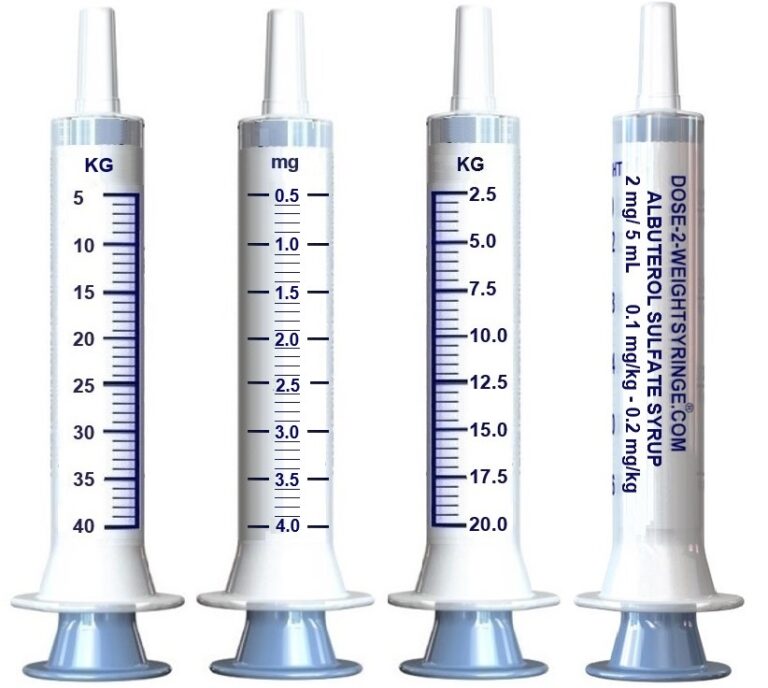
The current Prescribing Information (PI), for the administration of albuterol sulfate syrup 2mg/5mL for children 2 to 5 years of age, recites; a recommended dose of 0.1 mg/kg of body weight three times a day. For children who do not respond satisfactory to the initial starting dosage, the dosage may be increased stepwise to 0.2 mg/kg 3 times per day, but not to exceed a maximum of 4 mg (2 teaspoons) given three times a day.1
The PI and product label describe the syrup comprising 2 mg of albuterol sulfate in each 5 mL (teaspoonful).
Conversely, the PI does not describe the extrapolation of 0.1 mg or 0.2 mg from the 5 mL albuterol sulfate syrup or teaspoon, (1/10 and 1/20 of the teaspoon), nor the subsequent further calculation of it into milligram dose for kilogram body weight as prescribed.
Moreover, dozens of studies conclude that a household teaspoon is not an adequate measuring device.2 According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), among other health agencies, non-standard kitchen spoons are not recommended as a dosing apparatus for medicinal solutions. 2,3,4,5
The multi-dose Safe-2-Dose® Syringe is specifically calibrated to administer a patient specific dose of albuterol sulfate syrup to the optimal dose of 0.1 mg/kg or 0.2 mg/kg to an individualized body weight as recommended through one calibrated dispenser. The Dose-2-Weight Syringe allows for a singular preparation of either 0.1 mg/kg or 0.2 mg/kg to an individualized body weight as recommended.

