Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Suspension Dispenser
Pediatric Dosing Information
The current Prescribing Information (PI), for the administration of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim (200mg/40mg per 5 mL) suspension for pediatric patients with a body weight of 10 kg to 40 kg, recite a recommended dose 20.0 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole and 4.0 mg/kg trimethoprim every 12 hours for urinary tract infections, acute otitis media and shigellosis.1, This recommended dosing corresponds to 0.5 mL per kilogram body for all pediatric patient within this weight range. 1
The PI dosing chart (table 1), and product label further describe the dosing in teaspoons.1 Conversely, the PI does not describe the extrapolation of 20.0 mg/kg of sulfamethoxazole nor the 4.0 mg/kg of the trimethoprim from the 5 mL suspension and/or teaspoon.
Dozens of studies conclude that a household teaspoon is not an adequate measuring device.2 According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) and the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), among other health agencies, non-standard kitchen spoons are not recommended as a dosing apparatus for medicinal solutions. 2,3,4,5
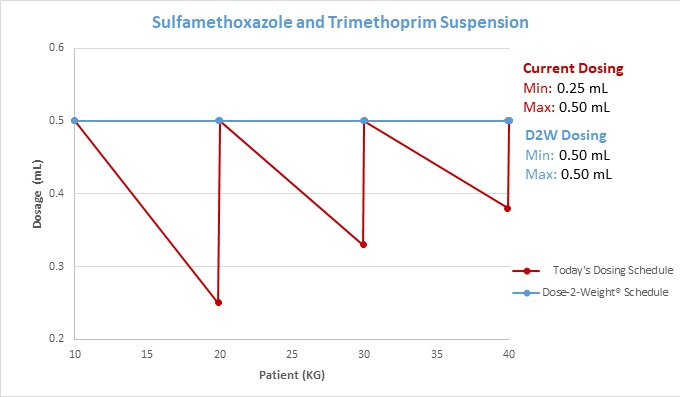
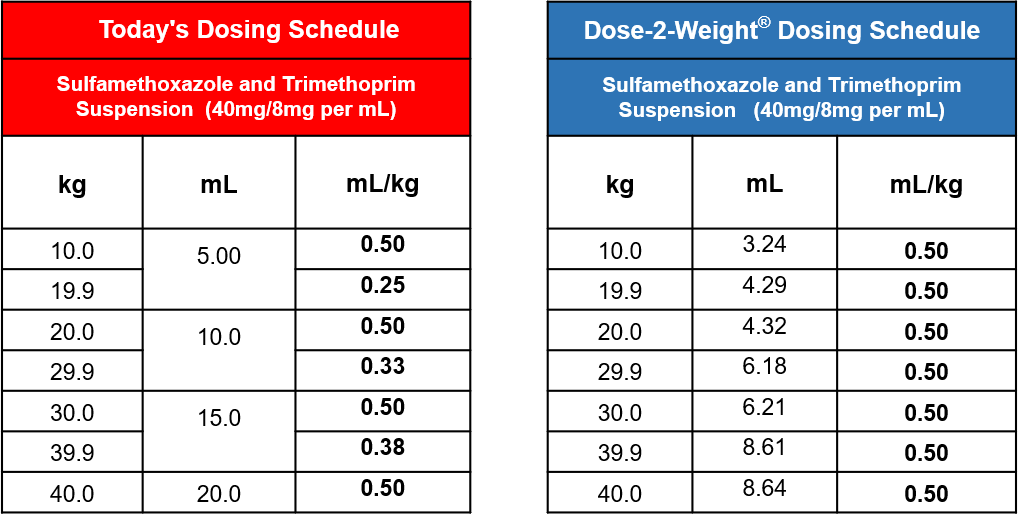
More importantly, the directions obviate any dosing directions for children between these defined weights ranges listed as well as any method for obtaining the optimal dosing for the 20.0 mg/kg of sulfamethoxazole nor the 4.0 mg/kg of the trimethoprim as prescribed. The preparation and administration directions solely provide for a recommended daily dose based upon a weight range in 10-kilogram increments and not to a child’s specific kg body weight, see table 1. This dosing regimen provides highly variable and perhaps subtherapeutic dosing to children within the defined weight ranges. The recommended dosing does not provide a consistent accurate milligram dose to a child’s individual body weight as clinically recommended. In addition, the variable dosing maybe exacerbated be the inaccuracy of measuring this suspension by household spoons, see table 2.
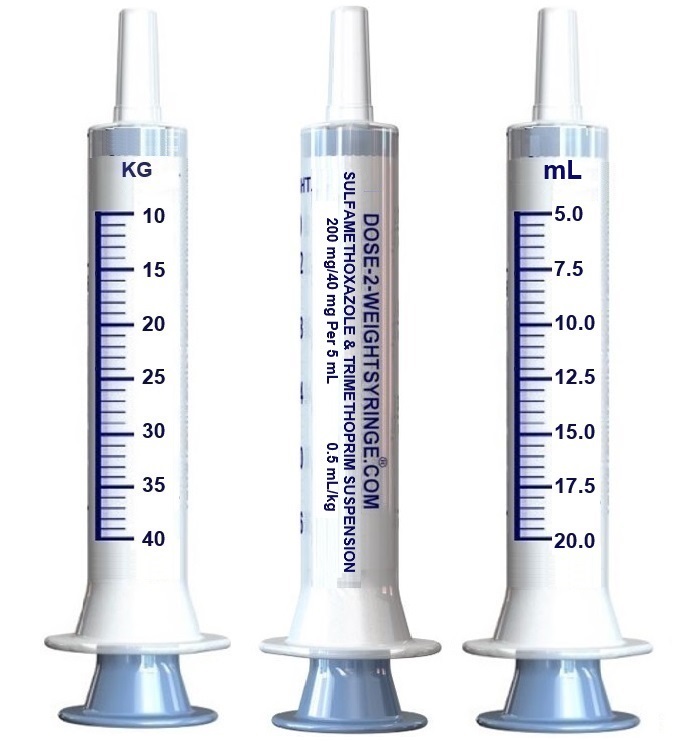
The Dose-Weight Syringe® is specifically calibrated to administer a patient specific dose of 0.5mL/kg providing for an optimal dose of 20.0 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 4.0 mg of trimethoprim to individual pediatric kilogram body weight.
Table 1.
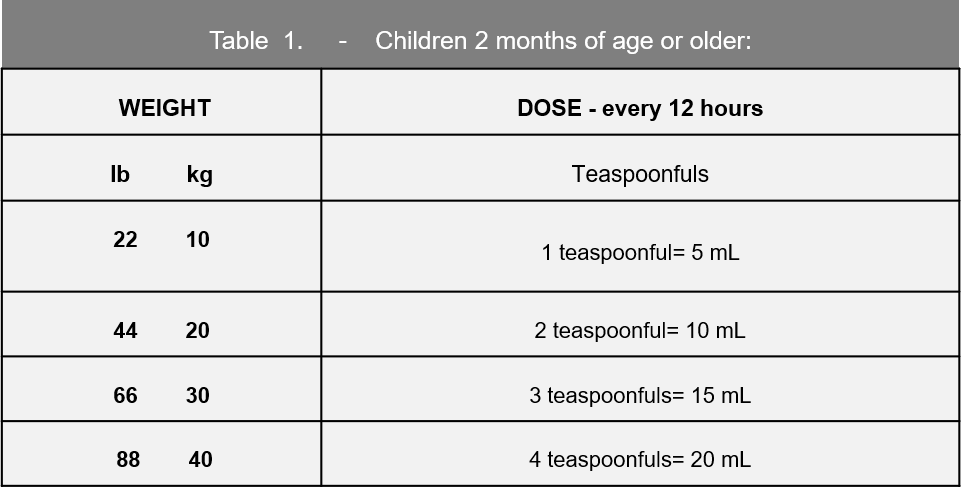
Table 2. Current dosing verses Dose-2-Weight ® Dosing